Trypanosomiasis, commonly known as “sleeping sickness” in humans and “nagana” in animals, is a neglected tropical disease caused by Trypanosoma parasites. These parasitic protozoans are transmitted primarily through the bites of infected tsetse flies (Glossina species) in sub-Saharan Africa. This disease not only causes significant human suffering but also imposes substantial socioeconomic burdens on communities that depend on agriculture and livestock.
This article delves into the impact of trypanosomiasis, highlights key facts, and briefly mentions supportive treatments like Nizonide 500mg, which plays a role in combating protozoan infections.
Understanding Trypanosomiasis
Trypanosomiasis manifests in two main forms
Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT)
Also known as sleeping sickness, HAT is caused by Trypanosoma brucei gambiense and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense.
- T. b. gambiense causes a chronic form of the disease prevalent in West and Central Africa.
- T. b. rhodesiense leads to a more acute form found in East and Southern Africa.
- Animal Trypanosomiasis: Also called nagana, this affects cattle, sheep, goats, and other domestic animals, reducing productivity and sometimes causing death.
- Without timely treatment, trypanosomiasis is almost always fatal.
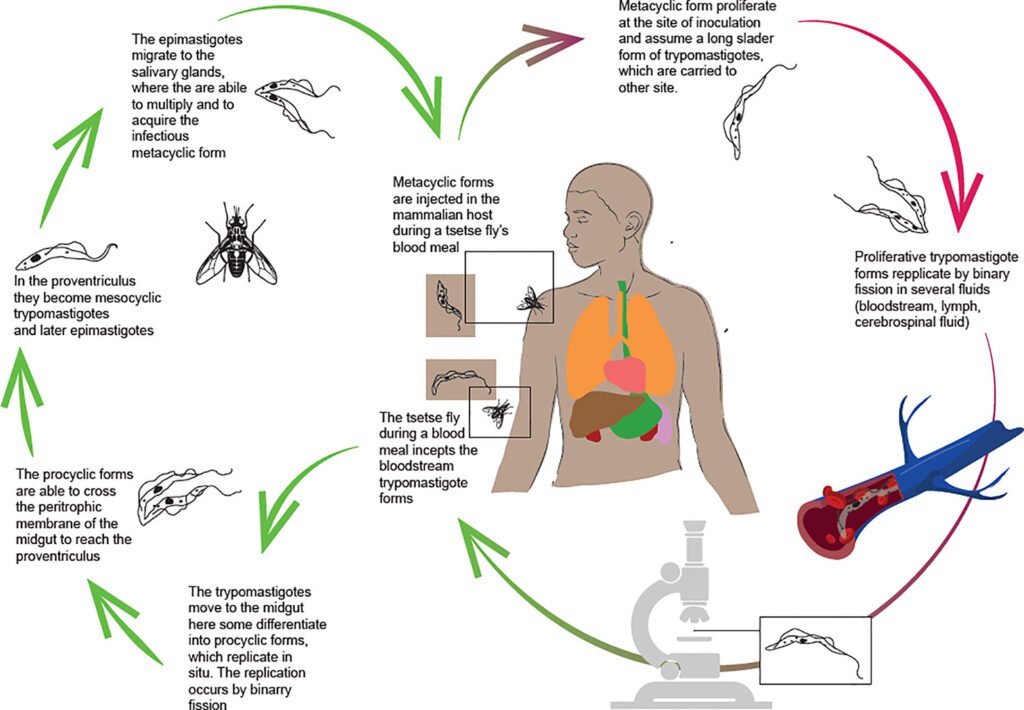
The Disease Mechanism
Once a tsetse fly bites a host, the parasites enter the bloodstream and replicate. In humans, the disease progresses through two stages
Haemolymphatic Stage
Parasites multiply in the blood and lymphatic system, causing fever, headaches, joint pains, and malaise.
Neurological Stage
Parasites cross the blood-brain barrier, leading to confusion, disrupted sleep cycles, and neurological damage. This phase is characteristic of the “sleeping” symptom, often leading to coma and death if untreated.
Epidemiological Impact
Human Health
In 2022, an estimated 20,000–25,000 cases of HAT were reported annually, with millions of people at risk across 36 African countries.
Effective surveillance and treatment programs by WHO and local governments have reduced new infections in recent years. However, challenges remain in remote regions where healthcare access is limited.
Agricultural Losses
Animal trypanosomiasis significantly impacts livestock productivity
Annual losses in livestock and agricultural productivity due to trypanosomiasis are estimated at $4.5 billion in Africa.
Affected animals produce less milk, have reduced fertility rates, and may die if untreated, threatening food security and economic stability.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis
- Early and accurate diagnosis is critical. Diagnostic methods include:
- Microscopic examination of blood smears.
- Serological tests like Card Agglutination Test for Trypanosomiasis (CATT).
- Molecular techniques such as PCR for precise identification.
Treatment
The choice of treatment depends on the disease stage
First-stage drugs
Pentamidine (for T. b. gambiense) and Suramin (for T. b. rhodesiense).
Second-stage drugs
Melarsoprol and eflornithine. The latter is often combined with nifurtimox in treatment protocols.
Role of Nizonide 500mg
Nizonide 500mg, containing nitazoxanide 500mg as the active ingredient, has shown efficacy against various protozoan infections. While primarily used for treating intestinal protozoa like Cryptosporidium and Giardia, it has gained attention in research for its broader antiparasitic and antiviral properties. As a supportive agent, it may be evaluated in experimental or adjunctive treatments for parasitic infections like trypanosomiasis. However, its direct application in trypanosomiasis management is still under study.
Challenges in Combatting Trypanosomiasis
Despite progress, several barriers hinder eradication efforts
Vector Control
Eliminating tsetse flies through traps, insecticides, and sterile insect techniques requires sustained effort and funding.
Access to Healthcare
Remote, underserved regions face challenges in disease detection and treatment delivery.
Drug Resistance
Parasites have developed resistance to some traditional medications, necessitating ongoing research into new therapies.
Climate Change
Shifts in climate may alter tsetse fly habitats, potentially expanding disease-endemic areas.
Global and Local Strategies for Control
Surveillance and Screening
Regular community screenings help detect cases early and prevent progression to the fatal neurological stage.
Vector Management
Techniques such as aerial spraying, tsetse traps, and introducing sterile male flies are being employed with varying success.
Vaccination and Drug Research
Developing vaccines remains a priority, although complex parasite biology poses challenges.
Community Awareness
Education campaigns encourage early reporting of symptoms and adherence to treatment.
Hope for the Future
International collaboration, spearheaded by organizations like WHO, has set ambitious targets to eliminate HAT as a public health concern by 2030. Advances in diagnostic tools, innovative treatments, and vector control methods fuel optimism.
Conclusion
Trypanosomiasis continues to pose severe health and economic challenges in Africa and beyond. Sustained efforts in surveillance, research, and community engagement are vital to controlling this devastating disease. While medications like Nizonide 500mg are not standard treatments for trypanosomiasis, their role in managing related parasitic infections highlights the importance of expanding our therapeutic arsenal.
Achieving elimination goals will require a coordinated global response, substantial investment, and a commitment to health equity for affected populations.