As networks scale and bandwidth demands grow, cable management becomes a critical part of maintaining performance and efficiency. Whether you’re dealing with a busy data center or a mid-size enterprise network, clean and reliable connections make a difference. That’s where an MPO to LC breakout cable fits in. It’s more than just a fiber cable — it’s a practical tool for managing complex fiber connections, saving space, and simplifying upgrades.
What is an MPO for LC Breakout Cable?
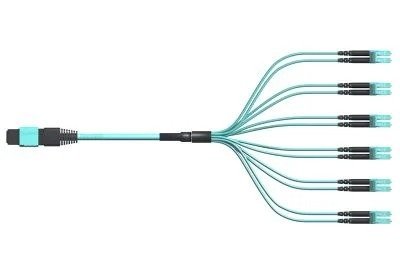
Let’s start with the basics. An MPO to LC breakout cable connects one MPO connector to multiple LC connectors. The MPO (Multi-Fiber Push On) side typically holds 8, 12, or 24 fibers bundled into a single connector. The LC side breaks those fibers out into individual links, usually in the form of duplex LC connectors. This allows you to take a high-density trunk connection and split it into multiple standard ports that connect directly to switches, transceivers, or patch panels.
Why Use a Breakout Cable Instead of Multiple Single Links?
Running individual fiber links can work, but once your system grows, that approach gets messy fast. You end up with a crowded rack, poor airflow, and a hard-to-maintain setup. Breakout cables solve that problem by consolidating those connections into a single, neat line that branches out only where necessary.
Here’s why that matters:
- Space Efficiency: Reduces the physical number of cables needed, freeing up valuable space in racks and trays.
- Faster Installation: One cable can replace several, cutting down setup time.
- Better Organization: Centralizes fiber routing, making systems easier to trace and manage.
- Improved Airflow: With fewer cables cluttering the rack, airflow improves, which can help keep devices cooler.
This makes them ideal in high-density environments where performance and maintenance go hand-in-hand.
Common Applications
You’ll often find breakout cables used in environments that rely on dense, high-speed fiber infrastructure:
- Data Centers: These cables help connect MPO-based trunk lines to equipment using LC ports, such as switches, servers, and patch panels.
- Enterprise Networks: Perfect for structured cabling systems that need scalability and simplicity.
- Storage Area Networks (SANs): Breakouts can make connections from a central switch to multiple storage nodes more efficient.
- High-Performance Computing Clusters: Where short, high-speed connections between nodes are necessary.
They’re especially useful in top-of-rack and end-of-row configurations where core switches use MPO ports but connected devices expect LC connectors.
Understanding the Connector Sides
- MPO Side
- The MPO connector is a compact, rectangular plug that can support multiple fibers in a single housing. These are available in different versions—most commonly 12-fiber and 24-fiber formats. The higher the fiber count, the more connections you can make from a single trunk.
- LC Side
- On the LC end, the breakout splits into multiple duplex connectors (each handling two fibers—one for transmit, one for receive). For example, an MPO-12 breakout would typically have six LC duplex connectors. Each LC connector can plug into a standard SFP module or port.
Polarity and Fiber Mapping
When using breakout cables, maintaining correct polarity is critical. Polarity refers to the alignment of the transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) signals between devices. If not managed properly, the signal won’t transmit correctly, and you’ll get errors or connection failures.
Breakout cables usually follow a standard mapping that ensures proper signal flow between the MPO and LC connectors. Always verify that your equipment and cabling match the required polarity type (Type A, B, or C).
Maintenance and Management
One underrated benefit of breakout cables is how they simplify maintenance. When cables are properly labeled and neatly routed, it’s easier to trace faults, test connections, and make changes. This cuts downtime and reduces the chance of mistakes. Also, having a defined structure to your cabling means fewer surprises. If a port goes bad or a device needs to be moved, you know exactly which LC connector to unplug, without disturbing unrelated links.
Final Thoughts
Fiber networks are growing more complex by the day, but that doesn’t mean your cabling has to follow suit. A structured approach using an MPO to LC breakout cable helps you keep control, even as your setup expands. It supports high-speed performance, keeps things organized, and saves time when you need to troubleshoot or upgrade. Whether you’re building a network from scratch or refining an existing one, this cable can play a key role in making your.