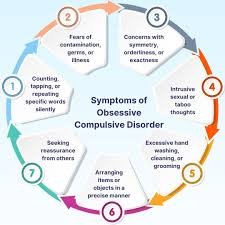
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) that individuals feel compelled to perform. It affects millions of people worldwide, causing significant distress and interference in daily life. While therapy and medication are common treatments, lifestyle changes can also play a vital role in managing OCD symptoms. In this article, we explore various lifestyle strategies that can support individuals living with OCD.
Understanding OCD: A Brief Overview
OCD is more than just excessive handwashing or organizing things perfectly. It involves a cycle of obsessions and compulsions that can become debilitating if left unmanaged. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder OCD might obsessively worry about contamination and feel compelled to wash their hands repeatedly to alleviate their anxiety. Understanding the nature of OCD is essential to adopting effective lifestyle changes.
The Role of Lifestyle in Mental Health
Mental health is deeply influenced by lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, sleep, and stress management. For individuals with OCD, incorporating positive habits can complement traditional treatments, reduce symptom severity, and improve overall well-being. Let’s delve into specific lifestyle changes that can make a difference.
1. Physical Activity: The Mind-Body Connection
How Exercise Helps
Regular exercise has been shown to reduce anxiety and improve mood by releasing endorphins and lowering stress hormone levels. For individuals with OCD, physical activity can also serve as a healthy distraction from obsessive thoughts.
Best Exercises for OCD
- Aerobic Exercises: Activities like running, cycling, or swimming improve cardiovascular health and boost mental clarity.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These practices combine movement with mindfulness, promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
- Strength Training: Building physical strength can increase confidence and resilience, indirectly benefiting mental health.
2. Nutrition and OCD: Fueling Mental Wellness
Key Nutrients for Mental Health
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, omega-3s can improve brain function and reduce anxiety.
- Vitamin D: Low levels of vitamin D are linked to mood disorders. Sunlight exposure and fortified foods can help.
- Magnesium: This mineral, found in leafy greens, nuts, and seeds, can calm the nervous system and ease anxiety.
Foods to Limit
- Caffeine: Excessive caffeine can heighten anxiety and trigger obsessive thoughts.
- Processed Foods: High sugar and unhealthy fats can negatively impact mood and energy levels.
3. Sleep Hygiene: The Foundation of Mental Health
Why Sleep Matters
Quality sleep is essential for emotional regulation and cognitive function. Sleep deprivation can exacerbate OCD symptoms, making intrusive thoughts harder to manage.
Tips for Better Sleep
- Establish a consistent bedtime routine.
- Avoid screens at least an hour before bed.
- Create a calming environment with dim lighting and soothing sounds.
4. Mindfulness and Meditation
Benefits for OCD
Mindfulness teaches individuals to observe their thoughts without judgment, reducing the power of obsessive thoughts. Meditation practices can help build a sense of calm and focus.
Techniques to Try
- Breathing Exercises: Focus on slow, deep breaths to ground yourself during moments of anxiety.
- Body Scans: This involves paying attention to physical sensations, and promoting relaxation.
- Guided Meditation Apps: Apps like Headspace or Calm offer specific meditations for anxiety and OCD.
5. Stress Management: Breaking the Cycle
How Stress Affects OCD
Stress can worsen OCD symptoms by increasing the frequency and intensity of intrusive thoughts. Learning to manage stress is crucial.
Practical Stress-Relief Strategies
- Time Management: Prioritize tasks and set realistic goals to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Relaxation Techniques: Progressive muscle relaxation or aromatherapy can ease tension.
- Hobbies and Creativity: Engaging in activities like painting, gardening, or playing music can provide a therapeutic outlet.
6. Social Connections and Support Systems
Importance of Community
Isolation can worsen OCD symptoms, while strong social connections can provide emotional support and encouragement.
Ways to Build Support
- Join support groups for individuals with OCD.
- Share your feelings with trusted friends or family members.
- Volunteer or participate in community activities to build connections.
7. Limiting Triggers: Creating a Safe Environment
Identifying Triggers
OCD triggers vary from person to person. Identifying these can help you create strategies to manage them effectively.
Creating a Supportive Environment
- Reduce exposure to known triggers when possible.
- Keep your living space organized and calming.
- Communicate your needs to those around you.
8. Cognitive Behavioral Strategies
Incorporating CBT Principles into Daily Life
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a gold-standard treatment for OCD. You can practice some of its principles in everyday life:
- Challenge irrational thoughts by questioning their validity.
- Gradually expose yourself to feared situations to build resilience.
- Replace compulsive behaviors with healthier habits.
9. The Role of Journaling in OCD Management
Benefits of Writing
Journaling can help you track triggers, identify patterns, and express emotions constructively. It’s also a way to celebrate progress.
How to Get Started
- Keep a daily log of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
- Write about moments of gratitude and positive experiences.
- Use prompts to explore specific challenges or breakthroughs.
10. Professional Help: Integrating Lifestyle Changes with Treatment
Collaborating with Healthcare Providers
While lifestyle changes can significantly benefit individuals with OCD, they should complement professional treatments like therapy and medication, not replace them. Share your lifestyle goals with your healthcare provider to ensure a holistic approach.
Combining Strategies
- Attend therapy sessions regularly while incorporating lifestyle changes.
- Use medication as prescribed, and discuss any concerns with your doctor.
Conclusion
Managing OCD symptoms requires a multi-faceted approach that combines professional treatment with supportive lifestyle changes. Regular exercise, balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, mindfulness practices, and stress management can all contribute to improved mental health. By making intentional, healthy choices, individuals with OCD can gain better control over their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.